Fermentation
It is not possible to process all products into animal feed. For example, products that contain meat. But we have a sustainable solution for these residual streams too: fermentation. Fermentation converts food waste into green energy. The products suitable for this process are listed below.
Conditions for successful fermentation
Practically all organic waste streams can be fermented, provided that certain conditions are met. Methane-forming bacteria multiply very slowly and in addition, it is easy to disrupt the biological processes of fermentation. Creating the optimal environment for these bacteria to flourish is a condition for success.
To ensure successful fermentation, products must be:
- Clean:
- Free of any packaging material;
- Free of other contamination or foreign matter such as wood or sand;
- Fresh;
- Able to be processed quickly.
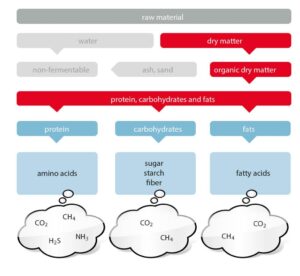
Which raw materials are suitable for fermentation?
Raw materials are made up of fermentable and non-fermentable, or difficult to ferment, parts: the fermentable nutrients in the material contribute to gas production.
Easily fermentable nutrients:
- Fat
- Starch
- Carbohydrates
Difficult/non-fermentable:
- Woody substances, such as lignin, and similar materials;
- Ash
- Sand
- Water
The influence of storage on gas production
Mould formation, heating and fermentation in storage tanks accounts for a lot of energy which is lost instead of being available for conversion into biogas. Toxins may also be formed which inhibit or destroy methane-forming bacteria. To maximise the fermentation yield potential, these conditions should be prevented.
Click to enlarge
More information on fermentation?
Would you like to know more about the suitability of products for fermentation or how to maximise the fermentation yield potential through efficient usage?